UE5のシェーダーを学ぶ
前回のUnityに続いて、今回は、UE5のシェーダーのコードを確認したいと思います。 UE5 はソースコードをすべて読むことができますので、まず、github からソースコードを取得します。
UE5 のソースコードをビルドして実行するまで
手順としては以下の通り。
- https://store.epicgames.com/ でEPICのアカウントを作成
- GitHub のアカウントを作成
- Epic のアカウント管理ページ(アプリとアカウント)から GitHub に接続
- https://github.com/EpicGames/UnrealEngine にアクセスして Clone する
- cd UnrealEngine
- Setup.bat
- GenerateProjectFiles.bat
- VisualStudio で UE5.sln を開いて、スタートアッププロジェクトを「UE5」に設定して、「Development Editor」と「Win64」で Build を実行
- UE5 をデバッグ実行
ビルドにはかなり時間がかかります。
UE5 のサンプルシーンを作成する
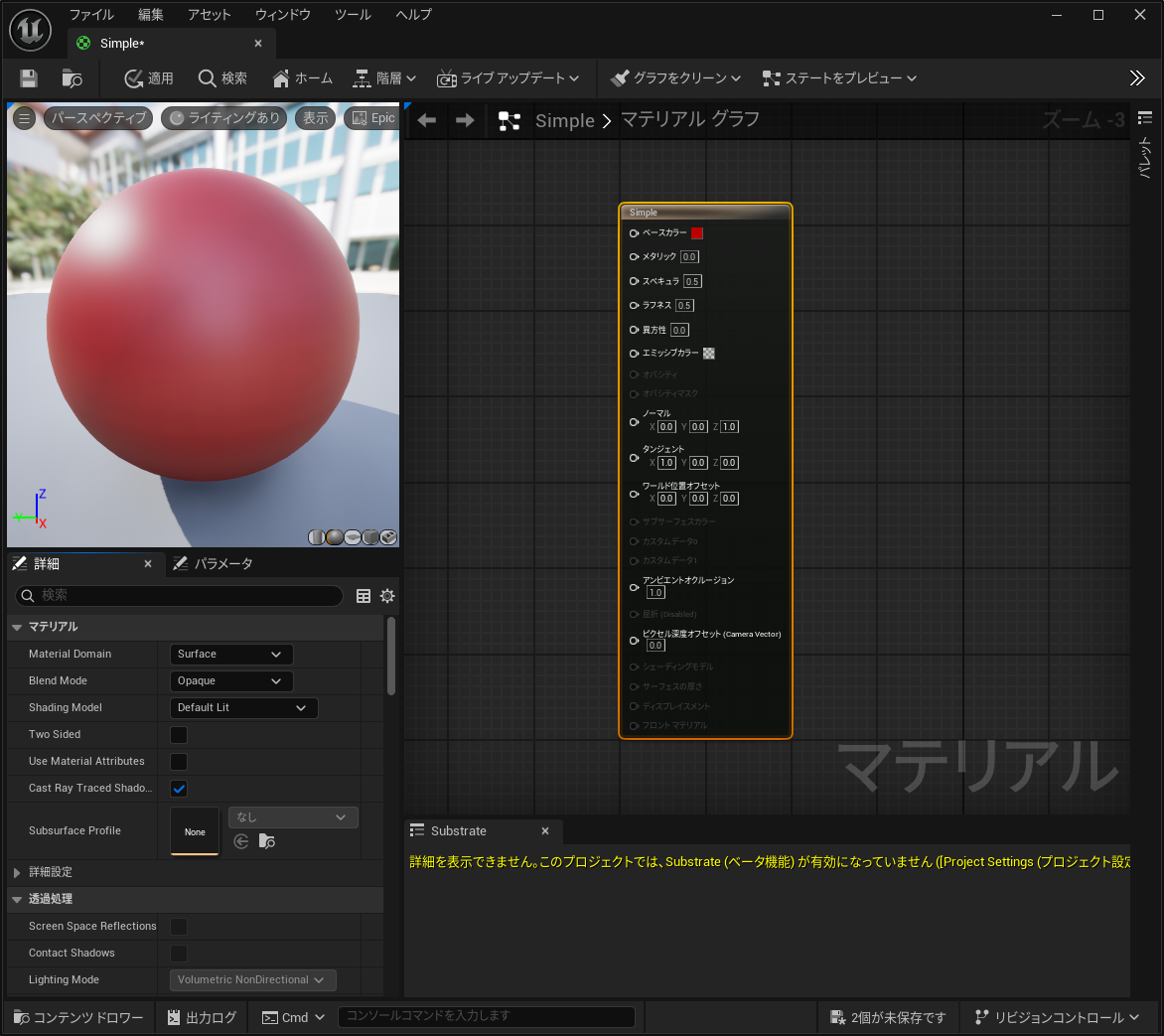
新規シーンを作成し、球を置き、Default Lit のマテリアルを作成します。
こんな感じです。
シェーダーのソースコードを探す
今回使用した UE5 のバージョンは、5.3.3-release です。
Engine/Shaders/Private
というフォルダににシェーダがあります。
UE5はデファードレンダリングが基本だと思いますので、GBufferに書き込むシェーダーと、GBufferの値からライティング計算を行うシェーダーの2種類を探します。
まず、GBufferに書き込むシェーダーですが、PixelShaderOutputCommon.ush に MainPS 関数があります。これがPixelShaderのメイン関数だと思います。 この中から、 BasePassPixelShader.usf の FPixelShaderInOut_MainPS 関数が呼ばれています。 ただ、GBufferに書き込むまではあまり処理としては面白味がないので、簡単に目を通す程度にしておきます。
次に、GBufferの値からライティング計算を行うシェーダーですが、 DeferredLightPixelShaders.usf に DeferredLightPixelMain 関数があります。これがライティング計算のメイン関数だと思います。
ここから結構深いのですが、
float4 Radiance = GetDynamicLighting(DerivedParams.TranslatedWorldPosition, DerivedParams.CameraVector, ScreenSpaceData.GBuffer, ScreenSpaceData.AmbientOcclusion, LightData, LightAttenuation, Dither, uint2(InputParams.PixelPos), SurfaceShadow);
このような呼び出しから、 DeferredLightCommon.ush のGetDynamicLighting 関数が呼ばれます。
/** Calculates lighting for a given position, normal, etc with a fully featured lighting model designed for quality. */
FDeferredLightingSplit GetDynamicLightingSplit(
float3 TranslatedWorldPosition, float3 CameraVector, FGBufferData GBuffer, float AmbientOcclusion,
FDeferredLightData LightData, float4 LightAttenuation, float Dither, uint2 SVPos,
inout float SurfaceShadow)
{
FLightAccumulator LightAccumulator = AccumulateDynamicLighting(TranslatedWorldPosition, CameraVector, GBuffer, AmbientOcclusion, LightData, LightAttenuation, Dither, SVPos, SurfaceShadow);
return LightAccumulator_GetResultSplit(LightAccumulator);
}
float4 GetDynamicLighting(
float3 TranslatedWorldPosition, float3 CameraVector, FGBufferData GBuffer, float AmbientOcclusion,
FDeferredLightData LightData, float4 LightAttenuation, float Dither, uint2 SVPos,
inout float SurfaceShadow)
{
FDeferredLightingSplit SplitLighting = GetDynamicLightingSplit(
TranslatedWorldPosition, CameraVector, GBuffer, AmbientOcclusion,
LightData, LightAttenuation, Dither, SVPos,
SurfaceShadow);
return SplitLighting.SpecularLighting + SplitLighting.DiffuseLighting;
}
さらに、同じファイル内で、AccumulateDynamicLighting 関数が定義されています。
FLightAccumulator AccumulateDynamicLighting(
float3 TranslatedWorldPosition, half3 CameraVector, FGBufferData GBuffer, half AmbientOcclusion,
FDeferredLightData LightData, half4 LightAttenuation, float Dither, uint2 SVPos,
inout float SurfaceShadow)
{
FLightAccumulator LightAccumulator = (FLightAccumulator)0;
half3 V = -CameraVector;
half3 N = GBuffer.WorldNormal;
BRANCH if( GBuffer.ShadingModelID == SHADINGMODELID_CLEAR_COAT && CLEAR_COAT_BOTTOM_NORMAL)
{
const float2 oct1 = ((float2(GBuffer.CustomData.a, GBuffer.CustomData.z) * 4) - (512.0/255.0)) + UnitVectorToOctahedron(GBuffer.WorldNormal);
N = OctahedronToUnitVector(oct1);
}
float3 L = LightData.Direction; // Already normalized
float3 ToLight = L;
float3 MaskedLightColor = LightData.Color;
float LightMask = 1;
if (LightData.bRadialLight)
{
LightMask = GetLocalLightAttenuation( TranslatedWorldPosition, LightData, ToLight, L );
#if ADAPTIVE_VOLUMETRIC_SHADOW_MAP
//LightAttenuation *= ComputeTransmittance(DerivedParams.TranslatedWorldPosition, LightData.TranslatedWorldPosition, 256);
LightAttenuation *= AVSM_SampleTransmittance(TranslatedWorldPosition, LightData.TranslatedWorldPosition);
#endif // ADAPTIVE_VOLUMETRIC_SHADOW_MAP
MaskedLightColor *= LightMask;
}
LightAccumulator.EstimatedCost += 0.3f; // running the PixelShader at all has a cost
BRANCH
if( LightMask > 0 )
{
FShadowTerms Shadow;
Shadow.SurfaceShadow = AmbientOcclusion;
Shadow.TransmissionShadow = 1;
Shadow.TransmissionThickness = 1;
Shadow.HairTransmittance.OpaqueVisibility = 1;
const float ContactShadowOpacity = GBuffer.CustomData.a;
GetShadowTerms(GBuffer.Depth, GBuffer.PrecomputedShadowFactors, GBuffer.ShadingModelID, ContactShadowOpacity,
LightData, TranslatedWorldPosition, L, LightAttenuation, Dither, Shadow);
SurfaceShadow = Shadow.SurfaceShadow;
LightAccumulator.EstimatedCost += 0.3f; // add the cost of getting the shadow terms
#if SHADING_PATH_MOBILE
const bool bNeedsSeparateSubsurfaceLightAccumulation = UseSubsurfaceProfile(GBuffer.ShadingModelID);
FDirectLighting Lighting = (FDirectLighting)0;
half NoL = max(0, dot(GBuffer.WorldNormal, L));
#if TRANSLUCENCY_NON_DIRECTIONAL
NoL = 1.0f;
#endif
BRANCH
if (LightData.bRectLight)
{
FRect Rect = GetRect( ToLight, LightData );
const FRectTexture SourceTexture = ConvertToRectTexture(LightData);
#if REFERENCE_QUALITY
Lighting = IntegrateBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, Rect, Shadow, SourceTexture, SVPos );
#else
Lighting = IntegrateBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, Rect, Shadow, SourceTexture);
#endif
}
else
{
Lighting = EvaluateBxDF(GBuffer, N, V, L, NoL, Shadow);
}
Lighting.Specular *= LightData.SpecularScale;
Lighting.Diffuse *= LightData.DiffuseScale;
LightAccumulator_AddSplit( LightAccumulator, Lighting.Diffuse, Lighting.Specular, Lighting.Diffuse, MaskedLightColor * Shadow.SurfaceShadow, bNeedsSeparateSubsurfaceLightAccumulation );
LightAccumulator_AddSplit( LightAccumulator, Lighting.Transmission, 0.0f, Lighting.Transmission, MaskedLightColor * Shadow.TransmissionShadow, bNeedsSeparateSubsurfaceLightAccumulation );
#else // SHADING_PATH_MOBILE
BRANCH
if( Shadow.SurfaceShadow + Shadow.TransmissionShadow > 0 )
{
const bool bNeedsSeparateSubsurfaceLightAccumulation = UseSubsurfaceProfile(GBuffer.ShadingModelID);
#if NON_DIRECTIONAL_DIRECT_LIGHTING
float Lighting;
if( LightData.bRectLight )
{
FRect Rect = GetRect( ToLight, LightData );
Lighting = IntegrateLight( Rect );
}
else
{
FCapsuleLight Capsule = GetCapsule( ToLight, LightData );
Lighting = IntegrateLight( Capsule, LightData.bInverseSquared );
}
float3 LightingDiffuse = Diffuse_Lambert( GBuffer.DiffuseColor ) * Lighting;
LightAccumulator_AddSplit(LightAccumulator, LightingDiffuse, 0.0f, 0, MaskedLightColor * Shadow.SurfaceShadow, bNeedsSeparateSubsurfaceLightAccumulation);
#else
FDirectLighting Lighting;
if (LightData.bRectLight)
{
FRect Rect = GetRect( ToLight, LightData );
const FRectTexture SourceTexture = ConvertToRectTexture(LightData);
#if REFERENCE_QUALITY
Lighting = IntegrateBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, Rect, Shadow, SourceTexture, SVPos );
#else
Lighting = IntegrateBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, Rect, Shadow, SourceTexture);
#endif
}
else
{
FCapsuleLight Capsule = GetCapsule( ToLight, LightData );
#if REFERENCE_QUALITY
Lighting = IntegrateBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, Capsule, Shadow, SVPos );
#else
Lighting = IntegrateBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, Capsule, Shadow, LightData.bInverseSquared );
#endif
}
Lighting.Specular *= LightData.SpecularScale;
Lighting.Diffuse *= LightData.DiffuseScale;
#if USE_LIGHT_FUNCTION_ATLAS
MaskedLightColor *= GetLocalLightFunctionCommon(TranslatedWorldPosition, LightData.LightFunctionAtlasLightIndex);
#endif
LightAccumulator_AddSplit( LightAccumulator, Lighting.Diffuse, Lighting.Specular, Lighting.Diffuse, MaskedLightColor * Shadow.SurfaceShadow, bNeedsSeparateSubsurfaceLightAccumulation );
LightAccumulator_AddSplit( LightAccumulator, Lighting.Transmission, 0.0f, Lighting.Transmission, MaskedLightColor * Shadow.TransmissionShadow, bNeedsSeparateSubsurfaceLightAccumulation );
LightAccumulator.EstimatedCost += 0.4f; // add the cost of the lighting computations (should sum up to 1 form one light)
#endif
}
#endif // SHADING_PATH_MOBILE
}
return LightAccumulator;
}
この関数内で、ShadingModels.ush の IntegrateBxDF 関数が呼ばれています。
FDirectLighting IntegrateBxDF( FGBufferData GBuffer, half3 N, half3 V, half3 L, float Falloff, half NoL, FAreaLight AreaLight, FShadowTerms Shadow )
{
switch( GBuffer.ShadingModelID )
{
case SHADINGMODELID_DEFAULT_LIT:
case SHADINGMODELID_SINGLELAYERWATER:
case SHADINGMODELID_THIN_TRANSLUCENT:
return DefaultLitBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_SUBSURFACE:
return SubsurfaceBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_PREINTEGRATED_SKIN:
return PreintegratedSkinBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_CLEAR_COAT:
return ClearCoatBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_SUBSURFACE_PROFILE:
return SubsurfaceProfileBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_TWOSIDED_FOLIAGE:
return TwoSidedBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_HAIR:
return HairBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_CLOTH:
return ClothBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
case SHADINGMODELID_EYE:
return EyeBxDF( GBuffer, N, V, L, Falloff, NoL, AreaLight, Shadow );
default:
return (FDirectLighting)0;
}
}
さらに同じファイルの中で、DefaultLitBxDF関数があります。
FDirectLighting DefaultLitBxDF( FGBufferData GBuffer, half3 N, half3 V, half3 L, float Falloff, half NoL, FAreaLight AreaLight, FShadowTerms Shadow )
{
BxDFContext Context;
FDirectLighting Lighting;
Lighting.Diffuse = 0;
Lighting.Specular = 0;
Lighting.Transmission = 0;
BRANCH
if (NoL > 0.0f)
{
#if SUPPORTS_ANISOTROPIC_MATERIALS
bool bHasAnisotropy = HasAnisotropy(GBuffer.SelectiveOutputMask);
#else
bool bHasAnisotropy = false;
#endif
float NoV, VoH, NoH;
BRANCH
if (bHasAnisotropy)
{
half3 X = GBuffer.WorldTangent;
half3 Y = normalize(cross(N, X));
Init(Context, N, X, Y, V, L);
NoV = Context.NoV;
VoH = Context.VoH;
NoH = Context.NoH;
}
else
{
#if SHADING_PATH_MOBILE
InitMobile(Context, N, V, L, NoL);
#else
Init(Context, N, V, L);
#endif
NoV = Context.NoV;
VoH = Context.VoH;
NoH = Context.NoH;
SphereMaxNoH(Context, AreaLight.SphereSinAlpha, true);
}
Context.NoV = saturate(abs( Context.NoV ) + 1e-5);
#if MATERIAL_ROUGHDIFFUSE
// Chan diffuse model with roughness == specular roughness. This is not necessarily a good modelisation of reality because when the mean free path is super small, the diffuse can in fact looks rougher. But this is a start.
// Also we cannot use the morphed context maximising NoH as this is causing visual artefact when interpolating rough/smooth diffuse response.
Lighting.Diffuse = Diffuse_Chan(GBuffer.DiffuseColor, Pow4(GBuffer.Roughness), NoV, NoL, VoH, NoH, GetAreaLightDiffuseMicroReflWeight(AreaLight));
#else
Lighting.Diffuse = Diffuse_Lambert(GBuffer.DiffuseColor);
#endif
Lighting.Diffuse *= AreaLight.FalloffColor * (Falloff * NoL);
BRANCH
if (bHasAnisotropy)
{
//Lighting.Specular = GBuffer.WorldTangent * .5f + .5f;
Lighting.Specular = AreaLight.FalloffColor * (Falloff * NoL) * SpecularGGX(GBuffer.Roughness, GBuffer.Anisotropy, GBuffer.SpecularColor, Context, NoL, AreaLight);
}
else
{
if( IsRectLight(AreaLight) )
{
Lighting.Specular = RectGGXApproxLTC(GBuffer.Roughness, GBuffer.SpecularColor, N, V, AreaLight.Rect, AreaLight.Texture);
}
else
{
Lighting.Specular = AreaLight.FalloffColor * (Falloff * NoL) * SpecularGGX(GBuffer.Roughness, GBuffer.SpecularColor, Context, NoL, AreaLight);
}
}
FBxDFEnergyTerms EnergyTerms = ComputeGGXSpecEnergyTerms(GBuffer.Roughness, Context.NoV, GBuffer.SpecularColor);
// Add energy presevation (i.e. attenuation of the specular layer onto the diffuse component
Lighting.Diffuse *= ComputeEnergyPreservation(EnergyTerms);
// Add specular microfacet multiple scattering term (energy-conservation)
Lighting.Specular *= ComputeEnergyConservation(EnergyTerms);
Lighting.Transmission = 0;
}
return Lighting;
}
あとは、同じファイルに、SpecularGGXがあって、PBRの計算が見つかりました。異方性がありとなしで2種類あるようです。
float3 SpecularGGX(float Roughness, float Anisotropy, float3 SpecularColor, BxDFContext Context, float NoL, FAreaLight AreaLight)
{
float Alpha = Roughness * Roughness;
float a2 = Alpha * Alpha;
FAreaLight Punctual = AreaLight;
Punctual.SphereSinAlpha = 0;
Punctual.SphereSinAlphaSoft = 0;
Punctual.LineCosSubtended = 1;
Punctual.Rect = (FRect)0;
Punctual.IsRectAndDiffuseMicroReflWeight = 0;
float Energy = EnergyNormalization(a2, Context.VoH, Punctual);
float ax = 0;
float ay = 0;
GetAnisotropicRoughness(Alpha, Anisotropy, ax, ay);
// Generalized microfacet specular
float3 D = D_GGXaniso(ax, ay, Context.NoH, Context.XoH, Context.YoH) * Energy;
float3 Vis = Vis_SmithJointAniso(ax, ay, Context.NoV, NoL, Context.XoV, Context.XoL, Context.YoV, Context.YoL);
float3 F = F_Schlick( SpecularColor, Context.VoH );
return (D * Vis) * F;
}
float3 SpecularGGX( float Roughness, float3 SpecularColor, BxDFContext Context, half NoL, FAreaLight AreaLight )
{
float a2 = Pow4( Roughness );
float Energy = EnergyNormalization( a2, Context.VoH, AreaLight );
#if SHADING_PATH_MOBILE
half D = D_GGX_Mobile(Roughness, Context.NoH) * Energy;
return MobileSpecularGGXInner(D, SpecularColor, Roughness, Context.NoV, NoL, Context.VoH, MOBILE_HIGH_QUALITY_BRDF);
#else
// Generalized microfacet specular
float D = D_GGX( a2, Context.NoH ) * Energy;
float Vis = Vis_SmithJointApprox( a2, Context.NoV, NoL );
float3 F = F_Schlick( SpecularColor, Context.VoH );
return (D * Vis) * F;
#endif
}
あとは、BRDF.ush で BRDF の細かい関数定義があります。
// GGX / Trowbridge-Reitz
// [Walter et al. 2007, "Microfacet models for refraction through rough surfaces"]
float D_GGX( float a2, float NoH )
{
float d = ( NoH * a2 - NoH ) * NoH + 1; // 2 mad
return a2 / ( PI*d*d ); // 4 mul, 1 rcp
}
// Anisotropic GGX
// [Burley 2012, "Physically-Based Shading at Disney"]
float D_GGXaniso( float ax, float ay, float NoH, float XoH, float YoH )
{
// The two formulations are mathematically equivalent
#if 1
float a2 = ax * ay;
float3 V = float3(ay * XoH, ax * YoH, a2 * NoH);
float S = dot(V, V);
return (1.0f / PI) * a2 * Square(a2 / S);
#else
float d = XoH*XoH / (ax*ax) + YoH*YoH / (ay*ay) + NoH*NoH;
return 1.0f / ( PI * ax*ay * d*d );
#endif
}
// Smith term for GGX
// [Smith 1967, "Geometrical shadowing of a random rough surface"]
float Vis_Smith( float a2, float NoV, float NoL )
{
float Vis_SmithV = NoV + sqrt( NoV * (NoV - NoV * a2) + a2 );
float Vis_SmithL = NoL + sqrt( NoL * (NoL - NoL * a2) + a2 );
return rcp( Vis_SmithV * Vis_SmithL );
}
// Appoximation of joint Smith term for GGX
// [Heitz 2014, "Understanding the Masking-Shadowing Function in Microfacet-Based BRDFs"]
float Vis_SmithJointApprox( float a2, float NoV, float NoL )
{
float a = sqrt(a2);
float Vis_SmithV = NoL * ( NoV * ( 1 - a ) + a );
float Vis_SmithL = NoV * ( NoL * ( 1 - a ) + a );
return 0.5 * rcp( Vis_SmithV + Vis_SmithL );
}
// [Heitz 2014, "Understanding the Masking-Shadowing Function in Microfacet-Based BRDFs"]
float Vis_SmithJoint(float a2, float NoV, float NoL)
{
float Vis_SmithV = NoL * sqrt(NoV * (NoV - NoV * a2) + a2);
float Vis_SmithL = NoV * sqrt(NoL * (NoL - NoL * a2) + a2);
return 0.5 * rcp(Vis_SmithV + Vis_SmithL);
}
// [Heitz 2014, "Understanding the Masking-Shadowing Function in Microfacet-Based BRDFs"]
float Vis_SmithJointAniso(float ax, float ay, float NoV, float NoL, float XoV, float XoL, float YoV, float YoL)
{
float Vis_SmithV = NoL * length(float3(ax * XoV, ay * YoV, NoV));
float Vis_SmithL = NoV * length(float3(ax * XoL, ay * YoL, NoL));
return 0.5 * rcp(Vis_SmithV + Vis_SmithL);
}
// [Schlick 1994, "An Inexpensive BRDF Model for Physically-Based Rendering"]
float3 F_Schlick( float3 SpecularColor, float VoH )
{
float Fc = Pow5( 1 - VoH ); // 1 sub, 3 mul
//return Fc + (1 - Fc) * SpecularColor; // 1 add, 3 mad
// Anything less than 2% is physically impossible and is instead considered to be shadowing
return saturate( 50.0 * SpecularColor.g ) * Fc + (1 - Fc) * SpecularColor;
}
float3 F_Schlick(float3 F0, float3 F90, float VoH)
{
float Fc = Pow5(1 - VoH);
return F90 * Fc + (1 - Fc) * F0;
}
UE5 は PBR計算の教科書のように整理されて書かれていますね。
今回はここまで。